Sam Bayer demonstrated his AGENT framework for collaborative conflict resolution at AgileRTP, including a live AI chatbot that guides users through workplace conflicts.
The AGENT Framework in Action: Conflict Resolution Meets AI at AgileRTP


Sam Bayer demonstrated his AGENT framework for collaborative conflict resolution at AgileRTP, including a live AI chatbot that guides users through workplace conflicts.
Claude Code’s new subagents feature changes everything about AI assistance. Here’s what specialized AI agents mean for developers and content creators.

A comprehensive, research-backed guide to mastering the evolution from traditional prompt engineering to context engineering, with detailed implementation examples and production-ready frameworks.

How a decade of trials—from Iceland’s government experiment to Microsoft’s corporate success to rigorous academic validation—proved the productivity paradox that working less can accomplish more.

A deep dive into the NYAI community’s 3-hour exploration of AI’s fundamental limitations, the compositionality crisis, and why we might need entirely new architectures for AGI.

A synthesis of months of deep philosophical discussions about AI consciousness, biological intelligence, and human transformation at NYC’s most thoughtful tech community.

Congressional Democrats demand answers from Palantir about surveillance ‘mega-database’ - validating months of investigative reporting that documented the company’s systematic expansion into domestic surveillance and war crimes operations.
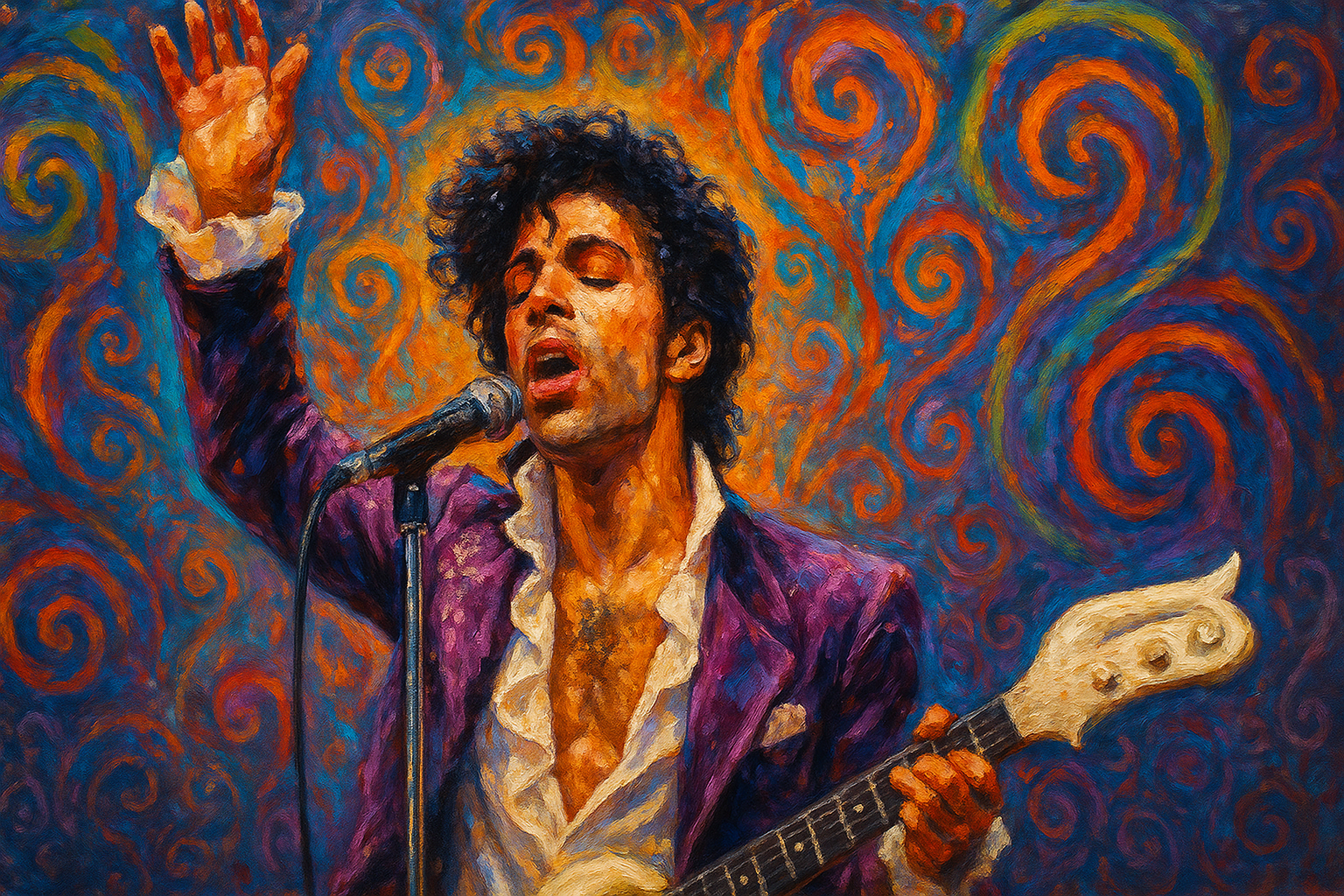

An exploration of Prince Rogers Nelson as a world-historical genius whose neurodivergent traits and revolutionary artistry placed him decades ahead of his time, told through the eyes of those who knew him and the fans who found themselves in his music.
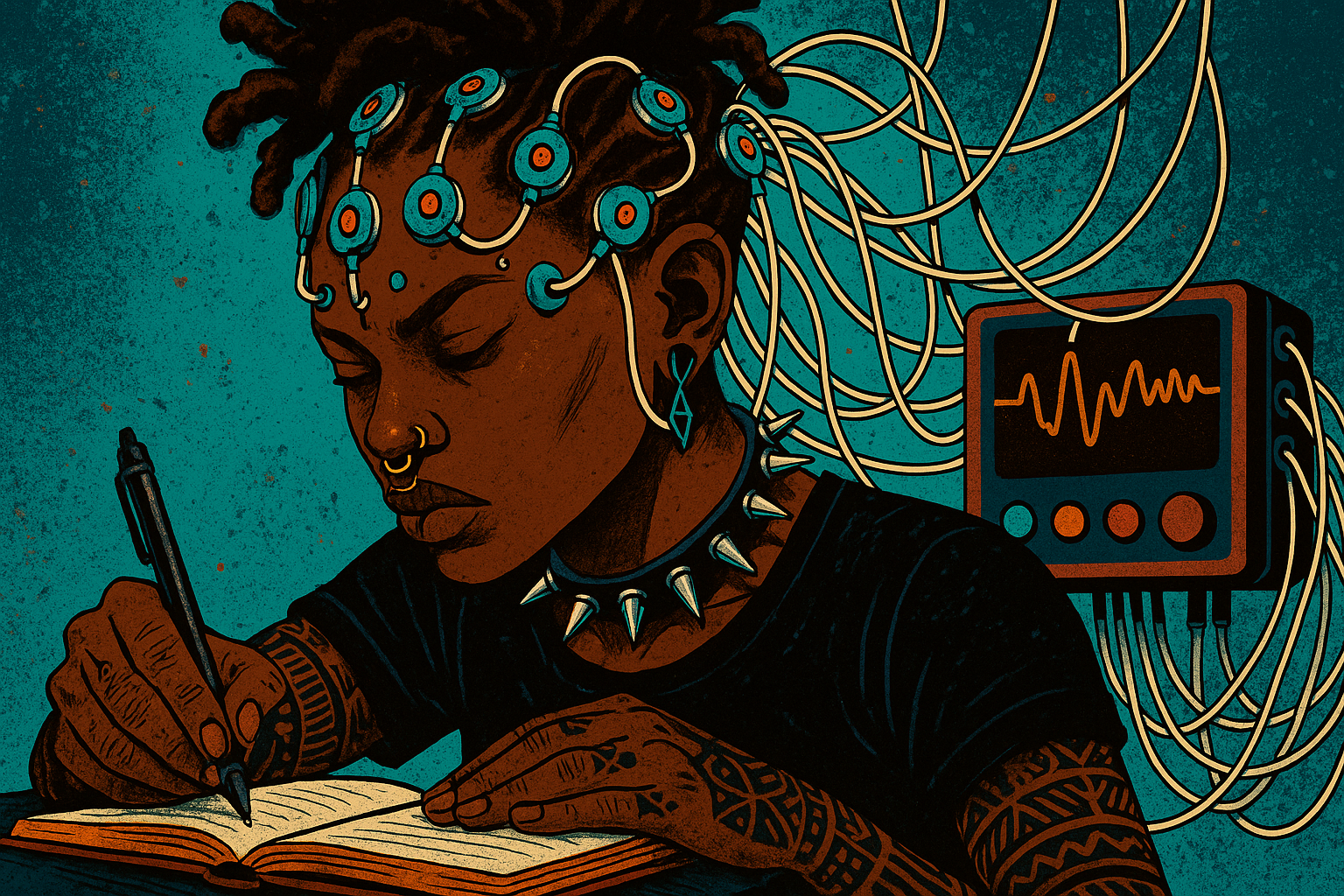

MIT researchers discovered that students using ChatGPT showed 55% weaker brain connectivity and couldn’t remember essays they ‘wrote’ hours before. The findings reveal a troubling new phenomenon: cognitive debt that could reshape how we think.
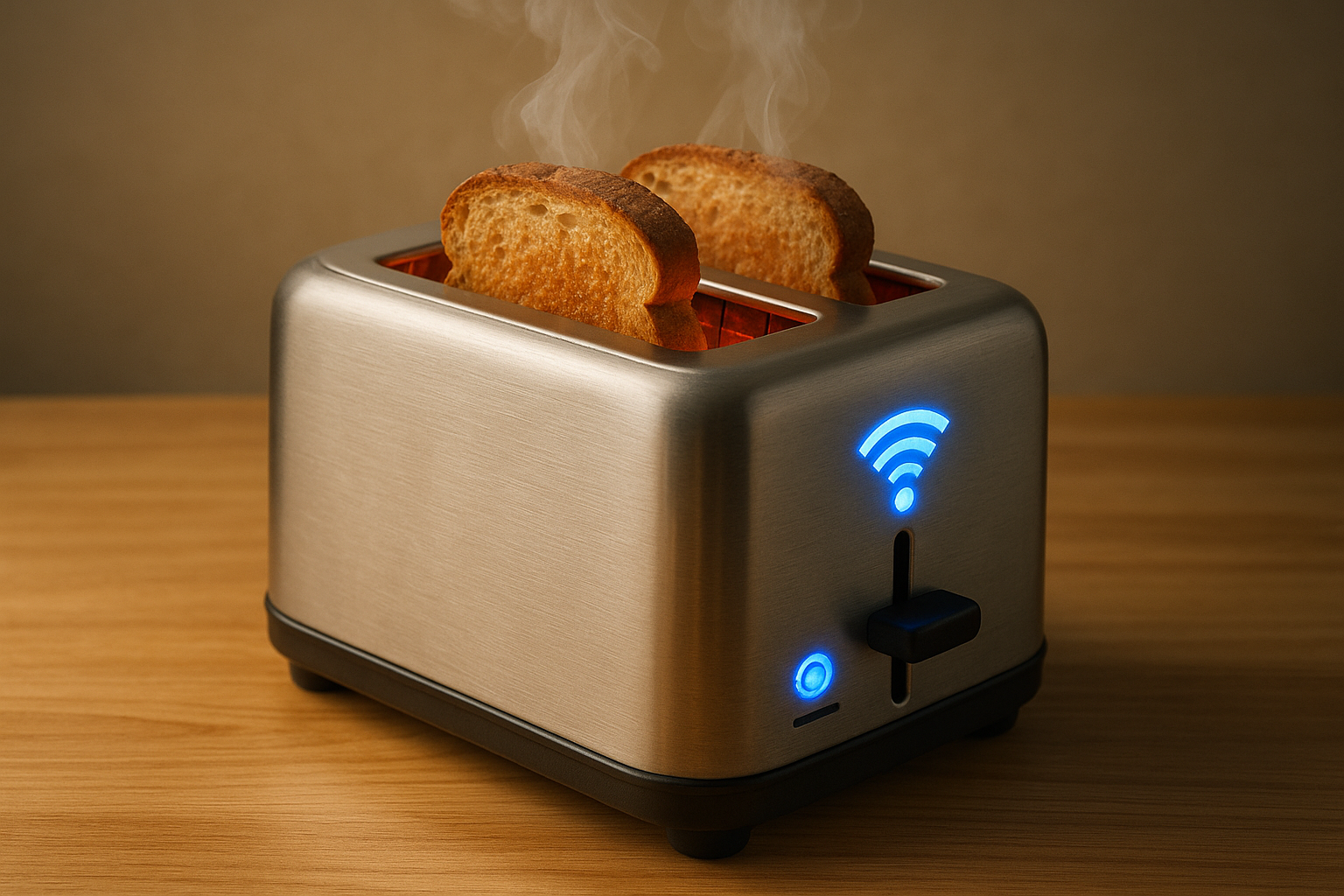

How $7 microcontrollers and accessible software are enabling ordinary people to retrofit household appliances with intelligent automation.